잿팩 컴포즈가 의존하고 있는 핵심 원칙을 검토
컴포저블 함수 자세히 살펴보기
컴포저블 함수의 구성 요소
- @Composable 어노테이션을 포함하는 코틀린 함수
- 컴포즈 컴파일러에 해당 함수가 데이터를 UI로 변환 한다는 것을 알림
코틀린 함수 시그니처
- 선택 사항인 가시성 변경자(private, protected, internal 또는 public)
- fun 키워드
- 함수명
- 매개변수 목록 또는 선택적 기본값 채택
- 선택 사항인 반환 타입
- 코드블록
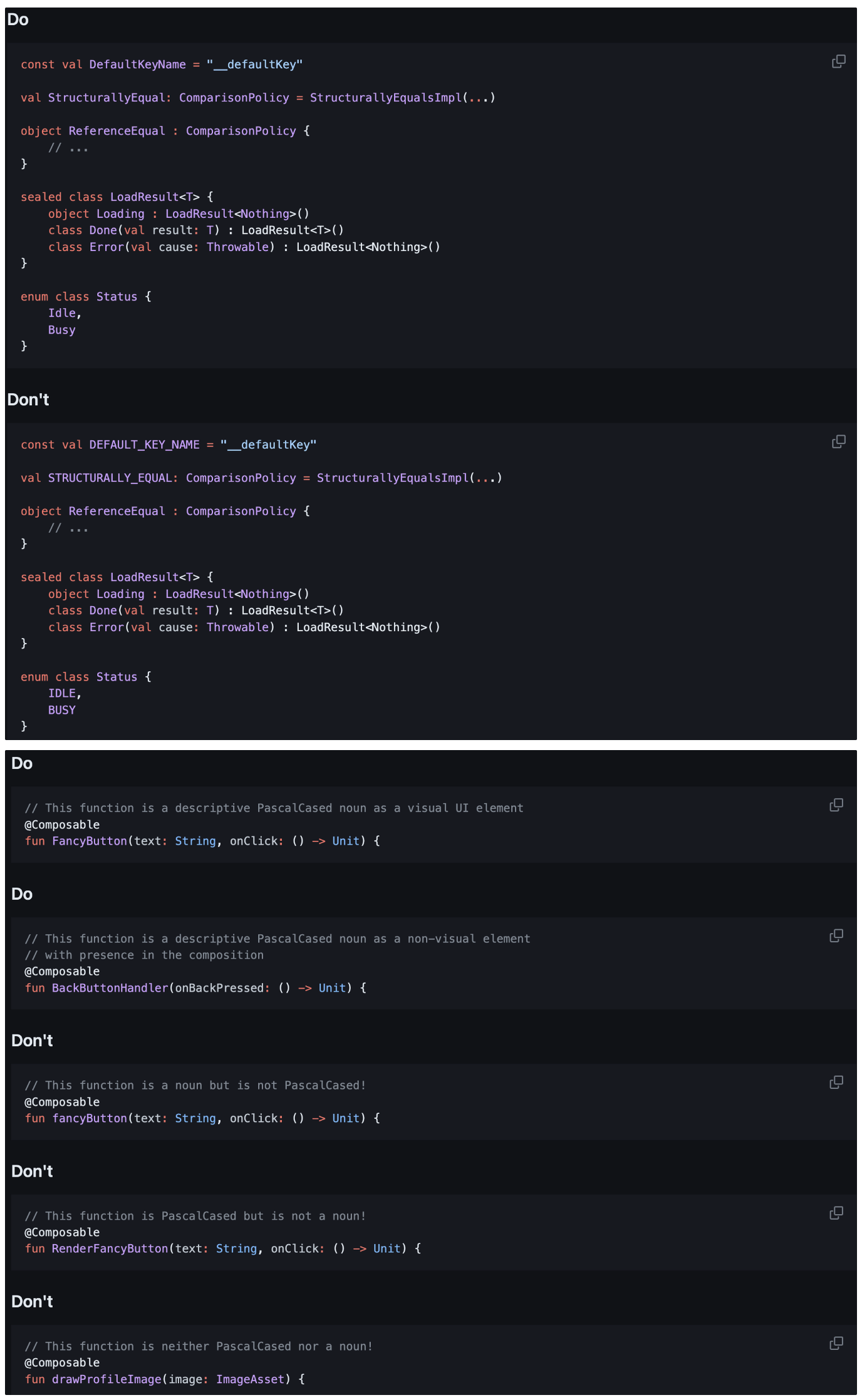
컴포저블 함수명은 파스칼(PascalCase) 표기법을 사용
- 대문자로 시작하지만 나머지 문자는 소문자로 나타낸다.
- 두 단어 이상으로 되어있다면
- 이름은 명사(Demo)
- 서술형 형용사를 접두어로 갖는 명사(FancyDemo)여야 한다.
- 다른 코틀린 함수와는 다르게 컴포저블 함수는 동사 또는 동사구(getDataFromServer)가 될 수 없다.
안내지침
@Composable
fun ShortColoredTextDemo(
text: String = "",
color: Color = Color.Black
) = Text(
text = text,
style = TextStyle(color = color)
)
- 컴포저블 함수에 전달하는 모든 데이터는 쉼표로 나눠진 목록으로 전달
- 값을 필요로 하지 않는다면 빈 괄호
- 매개변수는 이름: 타입 형태로 정의
- = ..을 사용한다면 기본값을 명시 → 기본값은 함수가 호출 됐을 때 변수값이 전달되지 않은 경우 사용
- 함수의 반환타입은 선택 사항 → 없다면 Unit
- 컴포저블 함수의 대부분은 어떠한 것도 반환할 필요가 없음. → 필요한 상황은 ‘값 반환’절에서 나옴
- 코틀린에서 하나의 표현식만 실행돼야 하는 경우 축약어를 제공 → 컴포즈 자체에서 빈번히 사용
내용을 출력하면 Unit을 반환
I/System.out: kotlin.Unit
- ColoredTextDemo()는 아무것도 반환하지 않았음에도 화면에는 텍스트가 출력된다.
- 컴포저블 함수가 Text()라는 또 다른 컴포저블 함수를 호출했기 때문에 발생
- 텍스트를 출력하는데 필요한 모든 것은 Text()내부에서 발생
- 컴포저블 함수의 반환값과는 관련이 없다.
UI 요소 내보내기
androidx.compose.material.Text()가 호출되면 어떤 일이 일어나는지 보자.
Text() 소스
@Composable
fun Text(
text: String,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
color: Color = Color.Unspecified,
fontSize: TextUnit = TextUnit.Unspecified,
fontStyle: FontStyle? = null,
fontWeight: FontWeight? = null,
fontFamily: FontFamily? = null,
letterSpacing: TextUnit = TextUnit.Unspecified,
textDecoration: TextDecoration? = null,
textAlign: TextAlign? = null,
lineHeight: TextUnit = TextUnit.Unspecified,
overflow: TextOverflow = TextOverflow.Clip,
softWrap: Boolean = true,
maxLines: Int = Int.MAX_VALUE,
minLines: Int = 1,
onTextLayout: (TextLayoutResult) -> Unit = {},
style: TextStyle = LocalTextStyle.current
) {
val textColor = color.takeOrElse {
style.color.takeOrElse {
LocalContentColor.current.copy(alpha = LocalContentAlpha.current)
}
}
// 맞춤 병합 구현을 작성하는 것이 좋습니다.
// 여기에 있는 모든 옵션이 기본값인 경우 재할당을 방지합니다.
val mergedStyle = style.merge(
TextStyle(
color = textColor,
fontSize = fontSize,
fontWeight = fontWeight,
textAlign = textAlign,
lineHeight = lineHeight,
fontFamily = fontFamily,
textDecoration = textDecoration,
fontStyle = fontStyle,
letterSpacing = letterSpacing
)
)
BasicText(
text = text,
modifier = modifier,
style = mergedStyle,
onTextLayout = onTextLayout,
overflow = overflow,
softWrap = softWrap,
maxLines = maxLines,
minLines = minLines
)
}
- textColor, mergedStyle을 정의하고 있음.
- androidx.compose.foundation.text.BasicText()에 변수를 전달
- 코드에서 BasicText()를 사용할 수도 있지만 Text()는 테마의 스타일 정보를 사용하기 때문에 가능하면 Text()를 선택
BasicText()는 즉시 CoreText()에 위임
@OptIn(InternalFoundationTextApi::class)
@Composable
fun BasicText(
text: String,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
style: TextStyle = TextStyle.Default,
onTextLayout: (TextLayoutResult) -> Unit = {},
overflow: TextOverflow = TextOverflow.Clip,
softWrap: Boolean = true,
maxLines: Int = Int.MAX_VALUE,
minLines: Int = 1
) {
// 여기에서 텍스트를 채널에 푸시하여 레이아웃을 미리 계산하는 것을 고려하십시오
// remember(text) { precomputeTextLayout(text) }
// 'heightInLines' 수정자 내에서 유효성 검사가 발생하는 텍스트 필드와 달리
// 텍스트에서 'maxLines'는 수정자에 의해 처리되지 않고
// 대신 StaticLayout으로 전달되므로 여기에서 유효성 검사를 수행합니다.
validateMinMaxLines(minLines, maxLines)
// selection registrar, SelectionContainer가 추가되지 않은 경우 주변 값은 null이 됩니다.
val selectionRegistrar = LocalSelectionRegistrar.current
val density = LocalDensity.current
val fontFamilyResolver = LocalFontFamilyResolver.current
// CoreText를 식별하는 데 사용되는 ID입니다.
// CoreText가 컴포지션 트리에서 제거된 다음 다시 추가되는 경우 ID는 동일하게 유지되어야 합니다.
//
// 입력 텍스트 또는 selectionRegistrar가 업데이트되면 선택 가능한 ID를 업데이트해야 합니다.
// 텍스트가 업데이트되면 이 CoreText에 대한 선택이 무효화됩니다.
// 그것은 완전히 새로운 CoreText로 취급될 수 있습니다.
// SelectionRegistrar가 업데이트되면 CoreText는 ID 충돌을 피하기 위해 새 ID를 요청해야 합니다.
// 잠재적인 버그입니다. selectableId는 텍스트가 생성될 때마다 여기에서 다시 생성됩니다.
// 변경되지만 TextState의 초기 생성에만 저장됩니다.
val selectableId = if (selectionRegistrar == null) {
SelectionRegistrar.InvalidSelectableId
} else {
rememberSaveable(text, selectionRegistrar, saver = selectionIdSaver(selectionRegistrar)) {
selectionRegistrar.nextSelectableId()
}
}
val controller = remember {
TextController(
TextState(
TextDelegate(
text = AnnotatedString(text),
style = style,
density = density,
softWrap = softWrap,
fontFamilyResolver = fontFamilyResolver,
overflow = overflow,
maxLines = maxLines,
minLines = minLines,
),
selectableId
)
)
}
val state = controller.state
if (!currentComposer.inserting) {
controller.setTextDelegate(
updateTextDelegate(
current = state.textDelegate,
text = text,
style = style,
density = density,
softWrap = softWrap,
fontFamilyResolver = fontFamilyResolver,
overflow = overflow,
maxLines = maxLines,
minLines = minLines,
)
)
}
state.onTextLayout = onTextLayout
controller.update(selectionRegistrar)
if (selectionRegistrar != null) {
state.selectionBackgroundColor = LocalTextSelectionColors.current.backgroundColor
}
Layout(modifier = modifier.then(controller.modifiers), measurePolicy = controller.measurePolicy)
}
- androidx.compose.foundation.text 패키지에 포함 되어있음.
CoreText()는 내부 컴포저블 함수로 앱에서는 사용할 수 없음.
CoreText()
- 수많은 변수를 초기화 하고 기억.
- 가장 중요한 부분은 또 다른 컴포저블 함수인 Layout()을 호출한다는 것.
Layout()
@Suppress("ComposableLambdaParameterPosition")
@UiComposable
@Composable inline fun Layout(
content: @Composable @UiComposable () -> Unit,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
measurePolicy: MeasurePolicy
) {
val density = LocalDensity.current
val layoutDirection = LocalLayoutDirection.current
val viewConfiguration = LocalViewConfiguration.current
ReusableComposeNode<ComposeUiNode, Applier<Any>>(
factory = ComposeUiNode.Constructor,
update = {
set(measurePolicy, ComposeUiNode.SetMeasurePolicy)
set(density, ComposeUiNode.SetDensity)
set(layoutDirection, ComposeUiNode.SetLayoutDirection)
set(viewConfiguration, ComposeUiNode.SetViewConfiguration)
},
skippableUpdate = materializerOf(modifier),
content = content
)
}
- androidx.compose.ui.layout 패키지에 포함
- 함수의 목적은 자식 요소의 크기와 위치를 지정
- ReusableComposeNode()를 호출
- androidx.compose.runtime 패키지에 포함
- 이 컴포저블 함수는 노드라고 하는 UI요소 계층 구조를 내보낸다.
ReusableComposeNode()
@Suppress("NONREADONLY_CALL_IN_READONLY_COMPOSABLE")
@Composable
inline fun <T : Any?, reified E : Applier<*>> ReusableComposeNode(
noinline factory: () -> T,
update: @DisallowComposableCalls Updater<T>.() -> Unit,
content: @Composable () -> Unit
) {
if (currentComposer.applier !is E) invalidApplier()
currentComposer.startReusableNode()
if (currentComposer.inserting) {
currentComposer.createNode(factory)
} else {
currentComposer.useNode()
}
Updater<T>(currentComposer).update()
content()
currentComposer.endNode()
}
- currentComposer는 androidx.compose.runtime.Composable.kt에 있는 최상위 변수
- 타입은 Composer로 인터페이스다
- 새로운 노드가 생성 돼야 할지 기존 노드를 재사용해야 할지 결정
- 그 뒤에 업데이트를 수행하고 마지막으로 content()를 호출하여 콘텐츠를 노드에 내보낸다.
Composer
- 잿팩 컴포즈 코틀린 컴파일러 플러그인에 의해 인식
- 코드 생성 헬퍼에 의해 사용
- 코드에서 직접 호출해서는 안됨
노드 (ComposeUiNode)
@PublishedApi
internal interface ComposeUiNode {
var measurePolicy: MeasurePolicy
var layoutDirection: LayoutDirection
var density: Density
var modifier: Modifier
var viewConfiguration: ViewConfiguration
/**
* Object of pre-allocated lambdas used to make use with ComposeNode allocation-less.
*/
companion object {
val Constructor: () -> ComposeUiNode = LayoutNode.Constructor
val VirtualConstructor: () -> ComposeUiNode = { LayoutNode(isVirtual = true) }
val SetModifier: ComposeUiNode.(Modifier) -> Unit = { this.modifier = it }
val SetDensity: ComposeUiNode.(Density) -> Unit = { this.density = it }
val SetMeasurePolicy: ComposeUiNode.(MeasurePolicy) -> Unit =
{ this.measurePolicy = it }
val SetLayoutDirection: ComposeUiNode.(LayoutDirection) -> Unit =
{ this.layoutDirection = it }
val SetViewConfiguration: ComposeUiNode.(ViewConfiguration) -> Unit =
{ this.viewConfiguration = it }
}
}
- 팩토리를 통해 생성되며 팩토리 인자로 전달 된다.
- update와 skippableUpdate 매개변수는 각각 코드를 전달 받는데,
- update : 노드에서 업데이트를 수행하는 코드 전달 받음
- skippableUpdate : 변경자를 조작하는 코드 전달 받음
- content는 자식 노드가 되는 컴포저블 함수를 포함
UI 요소를 내보내는 컴포저블 함수를 말할 때는 젯팩 컴포즈 내부에 있는 자료 구조에 노드가 추가된다는 것을 의미 → 결국 UI 요소를 화면에 나타나게 할 것
노드는 다음의 클래스나 인터페이스로 정의된 네 개의 프로퍼티를 갖는다.
- MeasurePolicy
- LayoutDirection
- Density
- Modifier
잿팩 컴포즈의 내부 동작의 일부로, 앱으로 노출되지 않기 때문에 코드에서 이를 다루지는 않는다.
위의 프로퍼티는 자주 볼 것이다.
정리 :
Layout()은 ReusableComposeNode에 ComposeUiNode.Constructor를 factory 인자로 전달
이 인자는 노드를 생성할 때 사용(currentComposer.createNode(factory))
→ 노드의 기능은 ComposeUiNode 인터페이스에 정의
값 반환
컴포저블 함수의 주목적이 UI를 구성하는 것이기 때문에 대부분은 반환할 필요가 없다.(반환타입 명시 안함)
그렇다면 언제 Unit이 아닌 다른값을 반환해야 할까?
- 나중에 사용할 수 있도록 상태를 유지하고자 remember { } 를 호출,
- strings.xml 파일에 저장된 문자열에 접근하고자 stringResource()를 호출
이들 모두 컴포저블 함수여야 한다.
stringResource() 소스, resources()
@Composable
@ReadOnlyComposable
fun stringResource(@StringRes id: Int): String {
val resources = resources()
return resources.getString(id)
}
@Composable
@ReadOnlyComposable
internal fun resources(): Resources {
LocalConfiguration.current
return LocalContext.current.resources
}
- resources() 도 컴포저블 함수다.
- LocalContext.current.resources를 반환
- androidx.compose.ui.platform 패키지에 폼함돼 있는 AndroidCompositionLocals.android.kt 파일에 정의된 최상위 변수다.
- 이 변수는 android.content.Context를 갖는 StaticProvidableCompositionLocal의 인스턴스를 반환 : 리소스에 접근 가능
- androidx.compose.ui.platform 패키지에 폼함돼 있는 AndroidCompositionLocals.android.kt 파일에 정의된 최상위 변수다.
- LocalContext.current.resources를 반환
사용자 인터페이스(UI) 구성과 재구성
잿팩 컴포즈는 앱 데이터가 변경돼야 하는 경우 개발자가 컴포넌트 트리를 변경하는 행위에 의존하지 않는다.
변화를 자체적으로 감지하고 영향을 받는 부분만 갱신
개념상 컴포즈는 변경사항이 적용돼야 할 때 UI전체를 다시 생성한다.
- 시간과 배터리, 처리능력 낭비
- 화면 깜빡거리는 현상을 통해 사용자가 인지할지도 모름.
프레임워크는 UI 요소 트리 중 갱신이 필요한 부분만 다시 생성되도록 노력하고있다.
빠르고 안정적인 재구성을 보장하려면 컴포저블 함수가 몇가지 간단한 규칙을 따르는지를 확인해야 한다.
- 컴포저블 함수 간 상태 공유
@Composable
fun ColorPicker(color: MutableState<Color>) {
val red = color.value.red
val green = color.value.green
val blue = color.value.blue
Column {
Slider(
value = red,
onValueChange = { color.value = Color(it, green, blue) })
Slider(
value = green,
onValueChange = { color.value = Color(red, it, blue) })
Slider(
value = blue,
onValueChange = { color.value = Color(red, green, it) })
}
}
왜 ColorPicker()가 MutableState<Color>로 감싼 색상을 전달 받았을까?
- ColorPicker()는 텍스트를 내보내지 않는다.
- (Column()안에서 발생)
- 색상변경은 ColorPicker() 내부에서 일어나므로 호출자에게 변화를 알려줘야만 한다.
- 일반적인 매개변수는 변경 불가능한 값이기 때문에 불가
- 전역으로 선언해 할수도 있지만 컴포즈에서 권고하지 않음.
- 컴포저블은 전역변수를 절대 사용하면 안 된다.
- 컴포저블 함수의 모습과 행위에 영향을 주는 모든 데이터는 매개변수로 전달하는것이 좋음
- 컴포저블 내부에서 변경된다면 MutableState를 사용
- 상태를 전달 받아 호출한곳으로 상태를 옮기는 것을 상태 호이스팅이라 부른다.
Column(
modifier = Modifier.width(min(400.dp, maxWidth)),
horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally
) {
val color = remember { mutableStateOf(Color.Magenta) }
ColorPicker(color)
Text(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.background(color.value),
text = "#${color.value.toArgb().toUInt().toString(16)}",
textAlign = TextAlign.Center,
style = MaterialTheme.typography.h4.merge(
TextStyle(
color = color.value.complementary()
)
)
)
}
- Column()이 처음 구성될 때 mutableStateOf(Color.Magenta)가 실행된다.
- 여기서 상태 생성 → 시간이 지남에 따라 변하는 앱 데이터
- remember?
- remember로 전달된 람다 표현식은 연산이라 부른다
- 실제 색상은 Value프로퍼티에 접근
- 따라서 background와 같은 매개변수에 변경할 수 있는 상태(color) 대신 **color.value(색상 값)**를 전달 (변경자)
- TextStyle() 내부에선 complementary()를 호출 중
- Color의 확장함수 (색상의 보색을 연산)
정리
- 컴포즈 UI는 컴포저블 함수의 중첩 호출로 정의
- 컴포저블 함수는 UI 요소 또는 UI 요소 계층 구조를 발행
- UI 를 처음 구성하는 것을 구성(composition)이라 부른다
- 앱 데이터 변경 시 UI를 재구성하는 것을 재구성(recomposition)이라 부른다.
- 재구성은 자동으로 발생한다.
액티비티 내에서 컴포저블 계층 구조 나타내기
ComponentActivity의 확장 함수인 setContent를 사용해 이 계층 구조를 액티비티에 임베디드 했다.
setContent
ComponentActivity.kt
public fun ComponentActivity.setContent(
parent: CompositionContext? = null,
content: @Composable () -> Unit
) {
val existingComposeView = window.decorView
.findViewById<ViewGroup>(android.R.id.content)
.getChildAt(0) as? ComposeView
if (existingComposeView != null) with(existingComposeView) {
setParentCompositionContext(parent)
setContent(content)
} else ComposeView(this).apply {
// Set content and parent **before** setContentView
// to have ComposeView create the composition on attach
setParentCompositionContext(parent)
setContent(content)
// Set the view tree owners before setting the content view so that the inflation process
// and attach listeners will see them already present
setOwners()
setContentView(this, DefaultActivityContentLayoutParams)
}
}
- parent : 널 값이 가능한 CompositionContext
- content : 선언하는 UI를 위한 컴포저블 함수
findViewById()는 액티비티가 이미 ComposeView의 인스턴스를 포함하는지 알아내기 위해 사용
- 포함 하면 setparentCompositionContext() 와 setContent() 호출
setparentCompositionContext()
- AbstractComposeView에 포함
- 뷰 구성시 부모가 되는 CompositionContext를 설정
- 컨텍스트가 null이면 자동으로 결정
- AbstractComposeView는 ensureCompositionCreate()라는 비공개 함수를 포함
- ComposeView쪽 setContent에서 ensureCompositionCreated 호출되며 wraper의 setContent호출하며 그 결과를 parent로서 resolveParentCompositionContext에 전달
AbstractComposeView.kt fun setParentCompositionContext(parent: CompositionContext?) { parentContext = parent } private var parentContext: CompositionContext? = null set(value) { if (field !== value) { field = value if (value != null) { cachedViewTreeCompositionContext = null } val old = composition if (old !== null) { old.dispose() composition = null // Recreate the composition now if we are attached. if (isAttachedToWindow) { ensureCompositionCreated() } } } } private fun resolveParentCompositionContext() = parentContext ?: findViewTreeCompositionContext()?.cacheIfAlive() ?: cachedViewTreeCompositionContext?.get()?.takeIf { it.isAlive } ?: windowRecomposer.cacheIfAlive() @Suppress("DEPRECATION") // Still using ViewGroup.setContent for now private fun ensureCompositionCreated() { if (composition == null) { try { creatingComposition = true composition = setContent(resolveParentCompositionContext()) { Content() } } finally { creatingComposition = false } } }
컴포저블 함수 행위 수정
컴포블의 시각적 형태나 행위는 매개변수나 변경자 또는 두 가지 모두를 통해 제어
- 종류 많아 익숙해지려면 시간이 필요
- 범주로 그룹화된 변경자 목록은 https://developer.android.com/jetpack/compose/modifiers-list 에서 확인
@Composable
fun OrderDemo() {
var color by remember { mutableStateOf(Color.Blue) }
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.padding(32.dp)
.border(BorderStroke(width = 2.dp, color = color))
.background(Color.LightGray)
.clickable {
color = if (color == Color.Blue)
Color.Red
else
Color.Blue
}
)
}
- Box는 클릭이 가능
- 테두리 색을 빨강 or 파랑 으로 변경
- .clickable { }을 .padding(32.dp) 앞으로 이동하면 간격에도 클릭 동작이 수행
변경자 동작 이해
companion object : Modifier {
override fun <R> foldIn(initial: R, operation: (R, Element) -> R): R = initial
override fun <R> foldOut(initial: R, operation: (Element, R) -> R): R = initial
override fun any(predicate: (Element) -> Boolean): Boolean = false
override fun all(predicate: (Element) -> Boolean): Boolean = true
override infix fun then(other: Modifier): Modifier = other
override fun toString() = "Modifier"
}
변경자를 적용하는 컴포저블 함수는 modifier 매개 변수로 변경자를 전달 받아야 하며 Modifier의 기본값을 할당 해야 한다.
- 아무것도 제공되지 않는다면 Modifier가 새로운 비어있는 체이닝으로 동작
- .background() 와 같은 변경자를 추가 할 수 있다.
규칙
- 그룹화 되어야 한다.
- 부모 변경자뒤에 나타나야 한다.
- UI요소에 특정 부분이나 자식 요소에 적용할 변경자를 인수로 전달 받는다면 자식의 이름을 접두어로 사용해야 한다. (titleModifier)
체이닝
- Modifier는 인터페이스이며 동반 객체
- then(0함수 : 두 변경자를 서로 연결
- Element 인터페이스는 Modifier를 확장했다
- 체인에 포함되는 단일 요소를 정의
변경자는 변경자 요소의 순서가 있는 변경 불가능한 컬렉션.
변경자 어떻게 구현
Modifier.background 소스
fun Modifier.background(
color: Color,
shape: Shape = RectangleShape
) = this.then(
Background(
color = color,
shape = shape,
inspectorInfo = debugInspectorInfo {
name = "background"
value = color
properties["color"] = color
properties["shape"] = shape
}
)
)
- background는 Modifier의 확장함수
- then()을 호출하고 결과(연결된 변경자)를 반환
- then은 order라는 한개의 매개 변수만 전달 받음. (현재 변경자와 연결돼 있어야 함)
DrawModifier : UI요소의 공간에 그림을 그릴 수 있다.
커스텀 변경자 구현
drawYellowCross() 소스
fun Modifier.drawYellowCross() = then(
object : DrawModifier {
override fun ContentDrawScope.draw() {
drawLine(
color = Color.Yellow,
start = Offset(0F, 0F),
end = Offset(size.width - 1, size.height - 1),
strokeWidth = 10F
)
drawLine(
color = Color.Yellow,
start = Offset(0F, size.height - 1),
end = Offset(size.width - 1, 0F),
strokeWidth = 10F
)
drawContent()
}
}
)
사용법
Text(
text = "Hello Compose",
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.drawYellowCross(),
textAlign = TextAlign.Center,
style = MaterialTheme.typography.h1
)
- drawYellowCross()는 Modifier의 확장 함수
- then()을 호출하고 결과를 반환
- drawContent()는 UI요소를 그리므로 언제 호출되느냐에 따라 앞 or 뒤에 나타남
- 마지막 커맨드라인에 위치하므로 맨위에 위치
- drawBehind { } 라는 변경자도 포함.
- 그리기 기본 요소를 포함할 수 있는 람다 표현식을 전달 받음.
- Modifier 기능을 통해서 Content의 뒷부분에 원하는 형태를 Canvas로 그릴 수 있다.
참조 : 젯팩 컴포즈로 개발하는 안드로이드 UI
'코틀린 & Java > 컴포즈 Compose' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 컴포즈(compose) 앱 스타일링 (0) | 2024.01.29 |
|---|---|
| 컴포즈(compose) 컴포저블 함수 상태 관리 (0) | 2023.09.05 |
| 컴포즈(Compose) UI 요소 배치 (0) | 2023.08.23 |
| 컴포즈(Compose) 선언적 패러다임 이해 (0) | 2023.08.16 |
| 컴포즈(Compose) 앱 빌드 (0) | 2023.08.16 |